Customer Service
March 24th 2020

An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) system is the central component of any well-designed power protection system. A UPS device will provide you with two primary functions:
There are high costs associated with any downtime caused by a power disturbance or interruption. They can also have dire results, including safety of employees, equipment damage, defective products, late shipments, or loss of business.
| Disturbance | Description |
|---|---|
| Blackouts
| Occurs when all power is lost, ranging from milliseconds to hours, or even days. To keep critical equipment running, a new power source must be provided either from stored energy (Uninterruptible Power Supply) or from a mechanical generator. |
| Brownouts within a circuit
| Overloading of electrical circuits can trigger a loss of power causing damage. During periods of high power demand, the power utility may intentionally reduce line voltage by up to 15%. Brownouts can last up to several days and create many forms of abnormal equipment behavior. |
| Spikes
| Sudden increases in voltage through lightning or power restoration after a widespread outage can damage equipment. Lasting only a few milliseconds, these induced voltage transient spikes are responsible for huge losses every year. |
| Power Surges
| A temporary rise in the voltage level lasting at least one half cycle. Voltage swells can be caused by high-power electric motors, switching off, and the normal cycling of HVAC systems. Most UPS in the market come with surge protection or automatic voltage regulation (AVR), which will take the edge off the power spike to protect your system components from being damaged. |
| Power Sag
| A short duration drop in voltage. Sags are usually caused by sudden nearby increases in the electrical load, and can degrade equipment performance for several seconds at a time. |
There are three basic types of UPS devices for protecting equipment: off-line, line-interactive, and on-line.
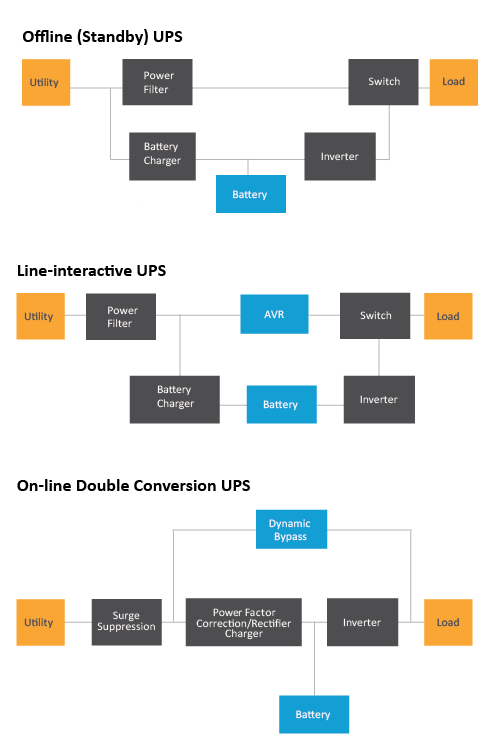
Offline (Standby) UPS
Standby UPS systems allow equipment to run on utility power until there is no input voltage detected, or a surge or sag is detected. It then powers the load using the inverter, which in turn is powered by the batteries. This option saves energy, but it also means the transfer to battery causes a very short interruption in power (typically 6-8 milliseconds). This is the simplest and most inexpensive UPS option available, however due to the UPS being offline it has limited power filtering capabilities and battery is used more frequently, which lowers battery life.
Line-Interactive UPS
Line-interactive UPS systems are similar to the off-line systems, however, it has an AVR (automatic voltage regulation) which regulates input utility voltage to guard against frequency abnormalities without switching to battery. This option is better at protecting equipment at a moderate cost and does not use its batteries nearly as often as the offline system, which extends battery life.
On-line Double Conversion UPS
In an on-line double conversion UPS, the input is first rectified and then re-converted into an alternating current with an inverter. This double-conversion ensures that equipment receives only clean electricity and that there is no transfer time when switching from the main power supply to the battery, as the output is always powered by the inverter. However, if the AC input supply falls out of predefined limits, the input rectifier shuts off and the output inverter begins drawing power from the battery instead. The UPS continues to utilize battery power until the AC input returns to normal tolerances. In the event of overloads or UPS system failure, this type of UPS also has an automatic bypass that ensures the load is powered by switching it directly at the input.
This option offers the best protection, seamless transition to battery and fully protects connected equipment. This in turn leads to less equipment failure, greatly extends battery life and reduces maintenance costs (as you need fewer UPS systems that need to be maintained).
An example of an online double conversion systems is the Liebert GTX5

Transfer time, sometimes also called switchover time, is the amount of time a UPS will take to switch from utility to battery supply. If equipment tolerance is below UPS transfer time, the UPS will not provide power in sufficient time in order to keep your equipment running.
SOLUTION: Vertiv UPS systems provide little to no transfer time when moving from utility power to battery depending on the type of UPS system you choose.
Offline systems transfer to battery causes a very short interruption in power (typically 6-8 milliseconds).
Line-interactive UPS systems typically transfer from line power to battery-derived power within two to four milliseconds, which is more than fast enough to keep all but a small percentage of the most power-sensitive equipment operating without interruption.
On-line UPS systems d do not have a transfer time because the inverter is already supplying power to the connected equipment load when an outage occurs.
Check user manuals of your equipment for exact transfer time tolerance. We also have technical experts that can help ensure you choose the right UPS system for you specific application needs.
When it comes to mission-critical applications, and the performance of the data center, downtime can be costly. Emerson Network Power study said that the average total cost per minute of an unplanned outage increased from $5,617 in 2010 to $7,908 in 2013 to $8,851 in 2016.
SOLUTION: Network/server UPS systems that use on-line operation and continuous double conversion provide the best protection and most reliable power available for critical systems. The double conversion process isolates equipment from power problems on the AC line and consistently delivers ideal output.
A factor to consider is the length of time that the load will operate on UPS-supplied power. Some loads may only require 15 to 30 minutes to be safely shutdown. Other loads, such as computers, servers, and telecommunication equipment may require power until utility power is restored.
SOLUTION:
Expandable-Runtime UPS Systems Many network/server UPS systems can also connect to one or more optional external battery packs to extend runtime. External batteries are large, costly and require periodic replacement, so it pays to provide a reasonable estimate of your runtime requirements. If your application requires an extremely long runtime, you may wish to supplement the UPS system with a standby generator.
Load Shedding Load shedding allows you to prioritize the battery backup runtime of your critical equipment by automatically turning off non-essential equipment during longer outages. Network/server UPS systems or connected PDUs that have controllable outlets allow you to set up load shedding.
Multi-voltage support is essential today to supply the right amount of electricity to computers and peripherals when the main electrical supply fails.
SOLUTION: Vertiv UPS outlets can be independently programmed to support different voltages (240/120, 208/120, 230/115, 220/110, or 200/100) for different equipment. This provides the flexibility to adapt multiple load requirements without the need to add additional transformers that will take up extra space and weight.
Routine preventative maintenance is critical to uptime and to protect sensitive electronics especially in mission-critical applications. At some point it will be necessary to take the UPS offline for maintenance and that means costly system downtime.
SOLUTION: Many Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system have addressed the down time associated with routine battery maintenance by offering a “hot swappable battery” feature integral to their UPS design. These batteries can be replaced without powering down the UPS system or your equipment to ensure no costly downtime.
How much wattage and capacity is needed?
You can estimate your UPS capacity requirement by adding up the wattage requirements of all the equipment you plan to connect to the UPS system. It is recommended that a UPS device be chosen with an output Watt Capacity 20-25% higher than that total. This helps the UPS handle fluctuations in power demand, leaves headroom for additional equipment and reduces the chance of overloads.
Although this method will provide a rough estimate of your UPS capacity requirements, we recommend that you confirm your estimate with the UPS manufacturer or talk to one of our Data Communications technical experts.
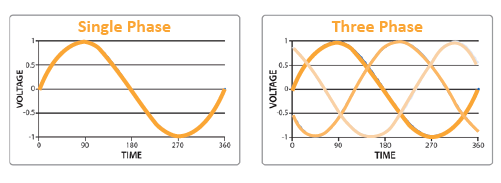
Single or 3 phase?
The power supply system is mainly classified into two types: single phase and three phase systems. The single phase is used in a place where less power is required and for running the small loads. The three phase is used in large industries, factories and in the manufacturing unit where a large amount of power is required. Vertiv UPS systems can be configured to supply either single or three-phase power depending on your application needs.

How much runtime is required for your equipment?
UPS runtime is how long the UPS unit will be able to power your equipment at the expected wattage level during a power outage.
To calculate battery/runtime, you need to know the minimum VA rating, the battery voltage, the amp-hour rating of the batteries, and the efficiency of the UPS.
Runtime in hours = (Battery voltage x Amp hour x Efficiency) / minimum VA rating
UPS system runtimes can be extended with external batteries and load shedding. However, for long term power outages generators are essential to keep equipment running.
Monitoring, Control and Management ?
Manual readings on a static report are no longer valid for today’s complex data center operations. Real-time data acquisition/monitoring, and ability to access and manage equipment remotely are a necessity to optimize their operations and avoid potential downtime.
Vertiv’s infrastructure monitoring, intelligent controls and centralized management systems work together to increase equipment availability, utilization and efficiency. IT departments can monitor/manage the UPS devices temperature, power, available runtime, current load and battery condition from anywhere and receive alerts if something goes wrong.
What input and output power do you need?
UPS Input: Before purchasing, make sure to determine the site’s electrical status of incoming utility, switchgear, panel-boards, voltage, loading, and dedicated circuit needs. This will help insure that the correct UPS device is chosen for your specific environment. It is also essential prior to buying that the UPS system will be able to connect to a compatible AC circuit.
UPS Output: Determining the distribution of power that you require ensures that UPS output matches the number of circuits, distance, and voltage requirements of your equipment.
What type of support and warranty is offered on a UPS?
Vertiv offers the industry’s best warranty. Their products come with a two year warranty and advanced UPS replacement in the event of any problems. An optional one year and three year extended warranty is also available for certain models which includes on-site system start up by a certified Vertiv Network Engineer, regular preventative maintenance, and on-site service incase a problem occurs.


Where do you plan to install the UPS System?
UPS systems come in a variety of sizes and formats from small desktop models to larger tower and rack-mount systems.Vertiv Racks can be used in conjunction to provide a compact and flexible spacing solution to meet changing room demands.
Rack-mount models can be mounted in standard 19″ rack enclosures and can require anywhere from 1U to 12U (U=rack space). They are typically used in server and networking applications.
Tower models stand upright on the ground or on a desk/shelf, and are typically used in network workstations or desktop computer applications.
Vertiv offers a vast range of UPS products from small systems to support desktop computers, through large scale three phase UPS for use in critical applications. Some other UPS systems applications include:
MODEL NUMBER | GXT5-1000LVRT2UXL |
|---|---|
| Image |    |
| Type | On-Line |
| Ratings (VA/W) | 1000VA/1000W |
| Warranty | Std. 3 year; Opt. 2 year |
| Dimensions W x D x H, in. | 16.9 x 15.7 x 3.4 |
| Weight lb.(kg) | 37 (16.8) |
| Battery Run Time (Full Load) | 6 minutes |
MODEL NUMBER | GXT5-1500LVRT2UXL |
|---|---|
| Image |   |
| Type | On-Line |
| Ratings (VA/W) | 1500VA/1350W |
| Warranty | Std. 3 year; Opt. 2 year |
| Dimensions W x D x H, in. | 16.9 x 18.5 x 3.4 |
| Weight lb.(kg) | 46.2 (21) |
| Battery Run Time (Full Load) | 5 minutes |
MODEL NUMBER | GXT5-3000LVRT2UXL |
|---|---|
| Image |    |
| Type | On-Line |
| Ratings (VA/W) | 3000VA/2700W |
| Warranty | Std. 3 year; Opt. 2 year |
| Dimensions W x D x H, in. | 16.9 x 21.3 x 3.4 |
| Weight lb.(kg) | 66(30) |
| Battery Run Time (Full Load) | 3 minutes |
For three-phase UPS devices, please contact the E.B. Horsman & Son Data Communications Division. Our technical staff will gladly work with Vertiv on engineering a three-phase UPS system for your application needs and specifications.
To learn more about Vertiv, a trusted partner of E.B. Horsman & Son for over 20 years, read our Manufacturer Spotlight.
If you require more information on UPS systems contact our technical staff. We will gladly answer any questions you may have and we can ensure you get the right system to protect your critical equipment.


Cable basket trays are more cost efficient, reliable, adaptable to change, and easy to maintain. Order your cable trays to protect your wiring…


Buy MOGAS to solve issues that routinely plague power plants – leaking valves, seat erosion, blown packing, and the inability to isolate critical…


Everything you need to shop for a Rittal Enclosure: from selecting the enclosure and cooling system to power distribution and…
Customer Service
1.888.467.7626